HDD and SSD
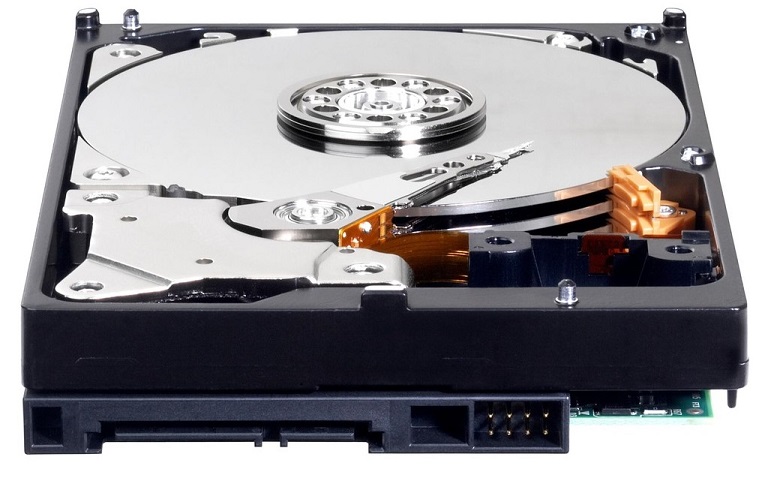
Standard HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
HDD hard disk drive is a device that uses magnetic media for storing the memory on a flexible backing, eg aluminum.
The disc structure consists of a plate or discs rotating in a hermetically sealed casing. For writing and reading data, the disk uses electromagnetic heads that float on the so-called air cushion.
The logical structure of the disk is divided into paths, sectors and cylinders.

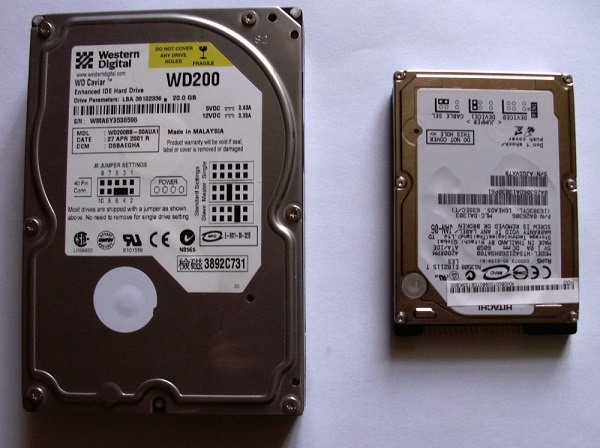
The most popular sizes of HDDs are 3.5 inches and 2.5 inches.

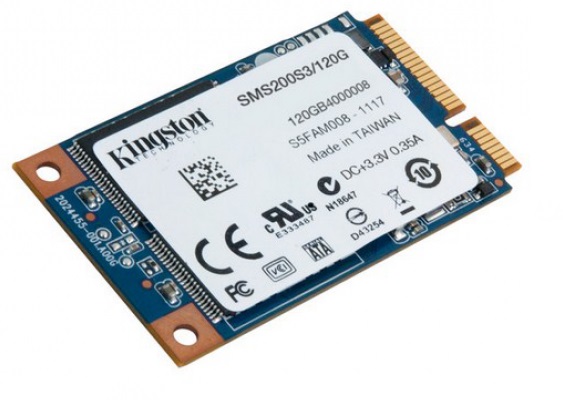
SSD (Solid State Drive)
SSD is an increasingly popular type of storage.
This type of disk is built on the basis of semiconductor flash memory. This disk has much shorter access time, greater resistance to mechanical damage, greater resistance to high temperatures and lower power consumption, all of which can be due to the fact that the SSD does not have any moving parts.
-OCZSSD3-2VTX120G.jpg)
Despite the undoubted advantages, SSD also has its drawbacks, first, high prices for HDD disks, the second disadvantage, unfortunately more serious, is the overall shorter durability, SSD has a more limited life.

Hard disk connectors
The hard disk has two basic connectors, power supply and data transfer.
The ATA / IDE connector was used first to transfer data, while the Molex power supply was used first.
The successor to the data transfer is SATA tape, there is also an eSATA version for connecting external drives.
The next step is the SCSI tape is a parallel bus used mainly for servicing servers, its successor is SAS tape
SSD disks can also use the PCI-Express, USB and fiber channel connectors.
How to care for hard drives
The basis for taking care of HDD is performing defragmentation from time to time, and less often the complete disk format.
Do not defragment on SSD disks.
To check the status of the disk, you can use dedicated applications, eg GsmartControl, HDTune.
CuR!05iTY
The largest SSD drive that has been constructed so far, has 60TB of capacity, the manufacturer is Seagate.